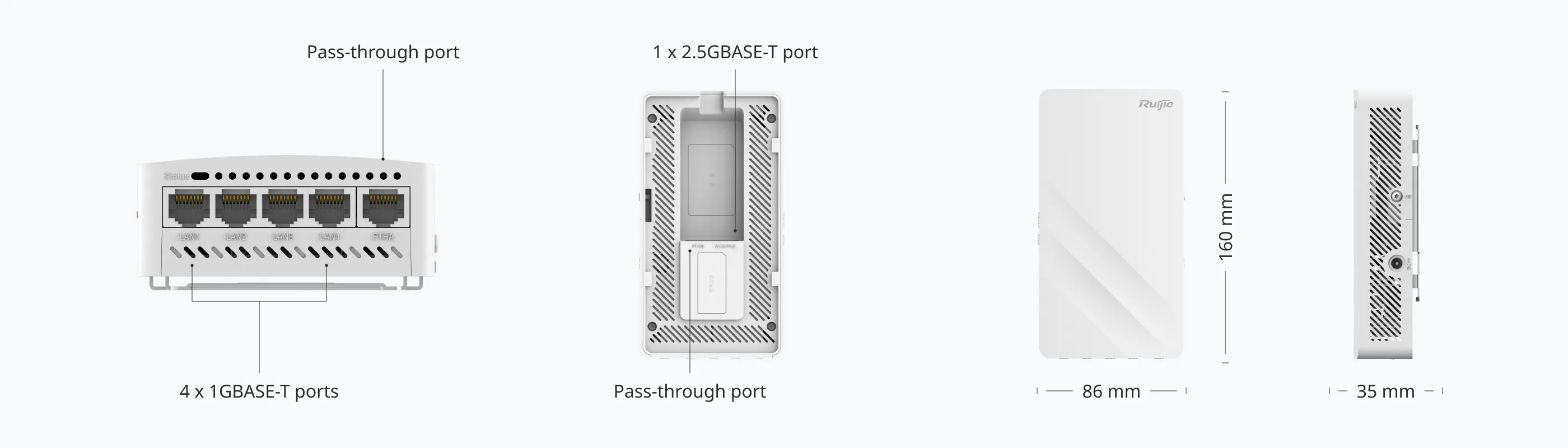
| Basic Function |
RG-AP1920 |
| Applicable software version |
RGOS11.9(6)W3B19 or later |
| WLAN |
| Maximum number of associated STAs |
256 (up to 128 STAs per radio) |
| Practical maximum client count indication (per device) |
64 |
| Maximum number of BSSIDs |
32 (up to 16 BSSIDs per radio) |
| Maximum number of WLAN IDs |
16 |
| STA management |
SSID hiding Band steering (preferential access to the 5 GHz radio) Each SSID can be configured with the authentication mode, encryption mechanism, and VLAN attributes independently. Remote intelligent perception technology (RIPT) Intelligent load balancing based on the STA quantity or traffic |
| STA limiting |
SSID-based STA limiting Radio-based STA limiting |
| Bandwidth limiting |
STA/SSID/AP-based rate limiting |
| CAPWAP |
IPv4/IPv6 CAPWAP Layer 2 and Layer 3 topology between an AP and an AC An AP can automatically discover the accessible AC. An AP can be automatically upgraded through the AC. An AP can automatically download the configuration file from the AC. CAPWAP through NAT MTU setting and fragmentation over CAPWAP tunnels Encryption over CAPWAP data tunnels Encryption over CAPWAP control tunnels |
| Data forwarding |
Centralized and local forwarding |
| Wireless roaming |
Layer 2 and Layer 3 roaming |
| Wireless locating |
Mobile unit (MU) location |
| Security and Authentication |
| Authentication and encryption |
Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) EXEC authorization, specifying source IP addresses of RADIUS packets, supporting authentication of other vendors, and built-in authentication server PSK, Web, 802.1X, WPA, WPA2, and WPA3 authentication QR code-based guest authentication, SMS-based authentication, and MAC authentication bypass (MAB) Data encryption: WEP (64/128 bits), WPA (TKIP), WPA-PSK, WPA2 (AES), and WPA3 |
| Data frame filtering |
Allowlist, static blocklist, and dynamic blocklist |
| WIDS |
Wireless Intrusion Detection System (WIDS) User isolation Rogue AP detection and containment |
| Dynamic Policy |
IP standard ACL, MAC extended ACL, IP extended ACL, expert ACL, and IPv6 ACL Time range-based ACL ACL based on a Layer 2 interface ACL based on a Layer 3 interface Ingress ACL based on a wireless interface Dynamic ACL assignment based on 802.1X authentication (used with an AC) |
| CPP |
CPU Protect Policy (CPP) |
| NFPP |
Network Foundation Protection Policy (NFPP) ARP attack defense, ICMP attack defense, and DHCP attack defense |
| Routing and Switching |
| MAC |
Static MAC address, MAC address filtering, MAC address limiting MAC address table size: 1,024 Maximum number of static MAC addresses: 1,024 Maximum number of filtered MAC addresses: 1,024 |
| Ethernet |
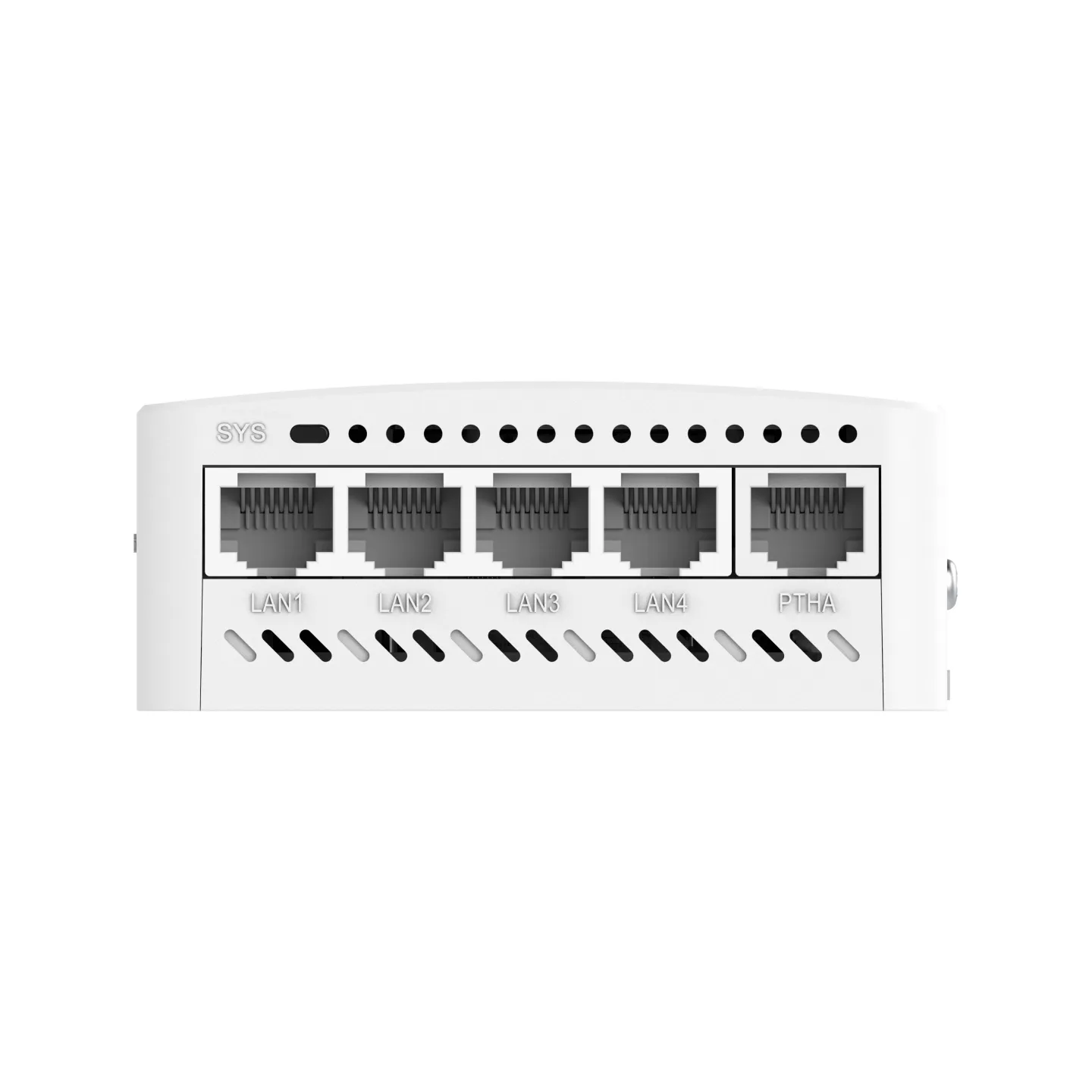
Jumbo frame length: 1,518 Full-duplex and half-duplex modes of interfaces Optical module information display, alarms about faults, and diagnosis parameter measurement (QSFP+/SFP+/SFP) |
| VLAN |
Interface-based VLAN assignment Maximum number of SVIs: 200 Maximum number of VLANs: 4,094 VLAN ID range: 1–4,094 |
| ARP |
ARP entry aging, gratuitous ARP learning, and proxy ARP Identification of IP address conflict among downlink users Maximum number of ARP entries: 1,024 ARP check |
| IPv4 services |
Static IPv4 address and DHCP-assigned IPv4 address Maximum number of IPv4 addresses configured on each Layer 3 interface: 200 NAT, FTP ALG, and DNS ALG |
| IPv6 services |
IPv6 addressing, Neighbor Discovery (ND), IPv6 ND proxy, ICMPv6, and IPv6 ping IPv6 DHCP client Maximum number of IPv6 addresses configured on each Layer 3 interface: 400 |
| IP routing |
IPv4/IPv6 static route Maximum number of static IPv4 routes: 1,024 Maximum number of static IPv6 routes: 1,000 |
| Multicast |
Multicast-to-unicast conversion |
| VPN |
PPPoE client IPsec VPN |
| Network Management and Monitoring |
| Network management |
NTP server and NTP client SNTP client SNMP v1/v2c/v3 Fault detection and alarming Information statistics collection and logging |
| Network management platform |
Web management (Eweb) |
| User access management |
Console, Telnet, SSH, FTP client, FTP server, and TFTP client |
| Switchover among Fat, Fit, and cloud modes |
When the AP works in Fit mode, it can be switched to Fat mode through an AC. When the AP works in Fat mode, it can be switched to Fit mode through the console port or Telnet. When the AP works in Cloud mode, it can be managed through WIS Cloud. |